- International News
- Thu-2021-08-26 | 02:40 pm
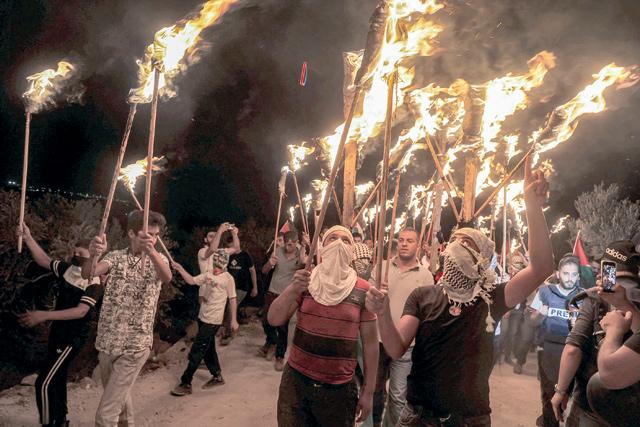
Nayrouz News Agency :
BEITA, Palestinian Territories — Using laser pointers and noisy horns to torment Jewish settlers across the valley, Palestinians in Beita have set themselves apart from others demonstrating against Israel’s occupation of the West Bank.
But beyond attention-grabbing tactics, protesters in the Palestinian town near Nablus insist their weeks-long campaign against the wildcat settlement of Eviatar is distinct for another reason.
They describe it as a grassroots movement, not inspired or directed by Fateh secularists who control the Palestinian Authority (PA) in the West Bank, or their rivals from the Islamist Hamas that runs the Gaza Strip.
"Here there is only one flag: That of Palestine. There are no factions,” Said Hamayel told AFP.
"We are doing from below what Palestinian leaders cannot do from above,” argued Hamayel, who said his 15-year-old son Mohammed was killed by Israeli forces gunfire in a mid-June protest.
Israeli forces said it had opened fire to suppress "rioters” who posed a grave threat to troops.
The Beita protests broke out in May as a group of hard-line settlers erected a Jewish community on a nearby hilltop.
All settlements are considered illegal under international law, but Israel has granted authorisation to such communities across the West Bank, a territory it has occupied since 1967.
But Eviatar was built without Israeli approval and the government struck a deal with settlers for their evacuation on July 2, while it studied the land to evaluate the prospect of eventual authorisation.
‘Popular resistance’
Israeli forces stationed at Eviatar since the settlers left have faced ongoing protests from the people of Beita, who number about 12,500 and say the surrounding land belongs to them.
More than 700 Palestinians have been injured and at least seven have been killed since the unrest erupted in May, according to the Palestinian health ministry.
Hamayel, who is still grieving over the loss of his son, voiced pride in what he termed the Beita "model”.
"The Israelis want to stamp out our new form of popular resistance. They are afraid of it.”
He said the Beita movement stood in contrast to the PA, led by 86-year-old president Mahmud Abbas, which "does nothing but issue statements” denouncing Israel’s occupation.
Palestinian politics have been fractured since 2007, the year Hamas took over Gaza after Fateh refused to recognise the Islamists’ election win.
Despite various reconciliation bids, bitter acrimony between the factions persists.
Fateh has remained entrenched in the West Bank, with Hamas running Gaza, but experts said events earlier this year altered sentiments among ordinary Palestinians.
Abbas cancelled the first scheduled Palestinian elections in 15 years, as street rallies in support of Palestinians facing Israeli eviction in occupied East Jerusalem gained momentum.
With tensions building in the Holy City and elsewhere, Israeli forces clashed with Palestinians at Jerusalem’s Al Aqsa Mosque compound, Islam’s third holiest site.
On May 10, Hamas fired rockets at Jerusalem, citing its mandate to defend Al Aqsa.
An 11-day Israel-Gaza conflict followed the Jerusalem rocket attack, with Hamas and other armed groups in the enclave launching thousands of munitions at Israel, which hit Gaza with hundreds of air strikes.
Common cause
The conflict and East Jerusalem protests revived a sense of common cause for young Palestinians that transcends allegiance to either Fatah or Hamas, said Jalaa Abu Arab, the 27-year-old editor of the Palestinian news site Dooz.
"For the first time in years the youth were not seeing themselves as victims anymore... there was the feeling that Palestinians were not just taking the fire and sitting, but rising and standing,” Abu Arab told AFP.
Young Palestinians have had enough with the "soft approach”, but that does not necessarily mean "they were in favour of Hamas”, he said.
Abu Arab referenced the death in Palestinian custody of Nizar Banat, a prominent critic of the PA, whose suspected killing by Palestinian security forces sparked protests.
Former Palestinian prime minister Salam Fayyad called the current situation "unprecedented”.
"I don’t know how far we are from really becoming a real crisis. It might already be [one] and it should be looked at by the leadership as a crisis.”
Speaking to a small group of reporters, he called for "a change of direction, beginning by listening to people, in particular the young people who are very frustrated with the occupation and the promises of freedom that remain unfulfilled”.
With Hamas-Fateh reconciliation seemingly out of reach and long-sought elections postponed indefinitely, Hamayel argued the "Beita model” could deliver change across the Palestinian territories.
"There are problems at the top, but here, on the ground, the Palestinians unite.”













